What is X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
15:49 - 18/05/2021
X-ray Diffraction (XRD) is used to study the crystal structure of materials.
Analysis of Aluminum ADC12, ADC6 According to JIS H 5302 Standard
Main Magnesium Alloys used in Industrial Production
Handheld XRF for Positive material identification
ElvaX ProSpector for Regulatory Compliance
What is X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)?
X-ray Diffraction (XRD) is used to study the crystal structure of materials because the X-ray wavelength (from 0.2 to 10 nm) is quite similar to about distance between atoms of a crystalline solid. This technique measures the average distance between layers or rows of atoms. XRD allows us to determine the orientation of a single crystal or grain and measure the size and shape of small crystalline regions.
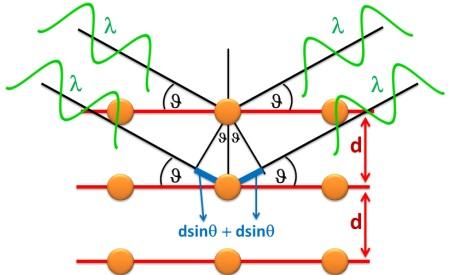
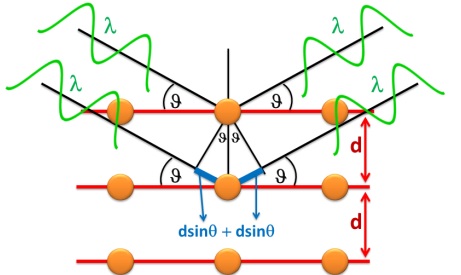
In XRD, an X-ray beam passes through a diverging slit and hits the sample surface, the X-ray beams arriving at this sample are scattered back by the periodic lattice, causing interference, X-ray diffraction. We will obtain an X-ray diffraction spectrum (peak) if the X-ray beam reaching the sample surface satisfies the BRAGG's law: 2dSinƟ = nλ.
Trong đó:
d: is the perpendicular distance between pairs of adjacent planes
Ɵ: is the angle of incidence or Bragg angle
n: n denotes an integer number, known as the order of the reflection
λ: is the wavelength of the beam
With the wavelength λ is a known constant, by changing the angle X-ray reference to atomic layer until diffraction obtained, we will calculate the coefficient d; the rows of lattice numbers h, k, l, compared with the International Center for Diffraction Spectroscopy Data (ICDD - International Center for Diffraction Data), we will determine the lattice structure; phase structure; identification and quantification of phase components; calculate crystal size and crystallinity,..
For more detailed:
https://web.stanford.edu/group/glam/xlab/MatSci162_172/LectureNotes/03_Bragg%20Law,%20KinDiff.pdf
Configuration of an X-ray diffraction spectrometer
The X-ray diffraction spectrometers we learn here are Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD). There are many types of XRD such as: Benchtop type; Floor type; Portable type, but basically includes the following main parts:
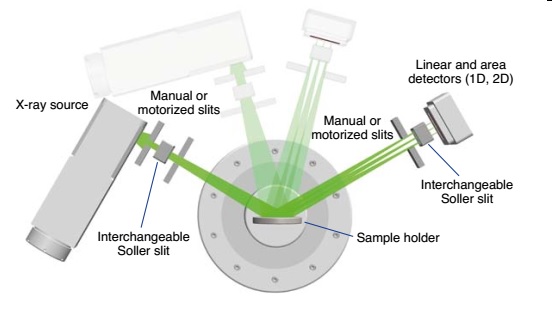 | 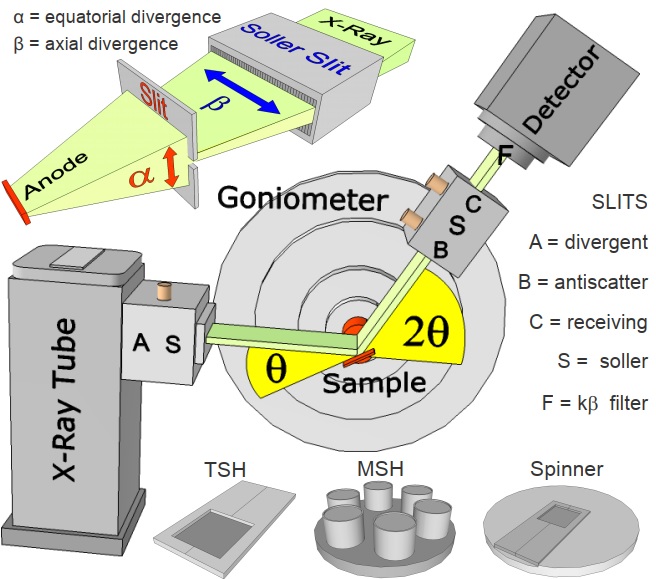 |
Theta - Theta | Theta – 2 Theta |
- X-ray source/X-ray tube/X-ray generator: with various power from 300W to 4kW; Voltage from 30kV to 80kV; 10mA to 80mA current suitable for many applications, with different types of models
- Soller slit: Guide the X-ray from the Source to the surface of the sample to be analyzed
- Sample holder: can hold 1 sample or turntable holds multiple samples; There are many types depending on the shape and size of the sample
- Goniometer:
+ Theta – Theta type: Sample holder is fixed; X-ray source and Detector move to ensure the angle of incidence and reflection are always equal (and equal to Ɵ).
+ Theta – 2 Theta: Fixed X-ray Source, Sample Holder and Detector moving to ensure the reflection angle (2Ɵ) is 2 times the incident angle (Ɵ).
+ Goniometer Scanning Angular Range from -1100 to +1680; Smallest selectable stepsize 0,00010
- Receiving Soller slit: Reflected X-ray acquisition: Directs the reflected X-rays from the sample surface to Detector
- Detector: Scintillation counter Nal or CeleriX 1D Hybrid Photon Counting (HPC) microstrip to obtain the X-ray diffraction spectrum; SDD detector can be installed for quantitative analysis of chemical elements in the sample.
- Computer set with software for control, analysis and processing of diffraction data
- Chiller for X-ray source cooling
Application of X-ray diffraction spectrometer
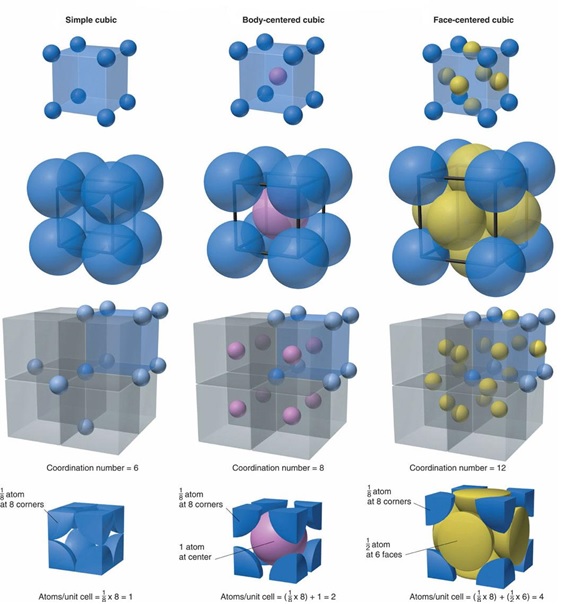
- Research on crystal lattice structure; calculate the size and crystallinity of the crystal
- Phase structure characterization and material phase composition quantification
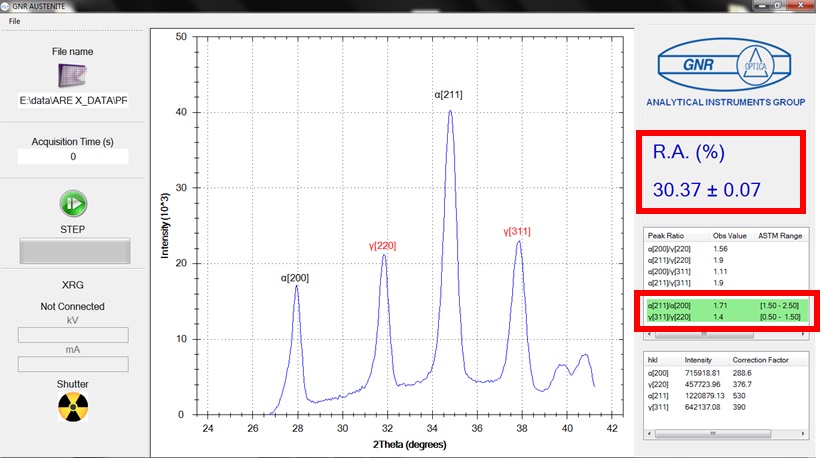
- Residual Stress and Retained Austenite Quantification
- …
For more detailed, please contact with HUST Vietnam!
