Adhesive curing technology with electromagnetic induction heat
10:03 - 05/01/2022
The great ideal solution is that the adhesive will cure within seconds using UV light. But this method only applies to translucent to transparent components, allowing UV light to pass through, and for visible locations, the temperature curing solution is the most optimal.
MEDMIX - Disposable Static Mixers
Cheaper and simpler micro-optics production
Adhesive for chip RFID in the smart card
ICA, ACA and TCA adhesives: Classification and applications
DELO ADHESIVES - HIGH SPEED CARRIER BONDING
Adhesive curing technology with electromagnetic induction heat
The technology of heating materials with electromagnetic induction heat from a high-frequency furnace is not too new, but its application for glue curing in electric motors or similar details still seems to be quite new. The following article will help readers better understand the glue curing technology by electromagnetic induction and why we should use this technology to alternate for a convection oven.
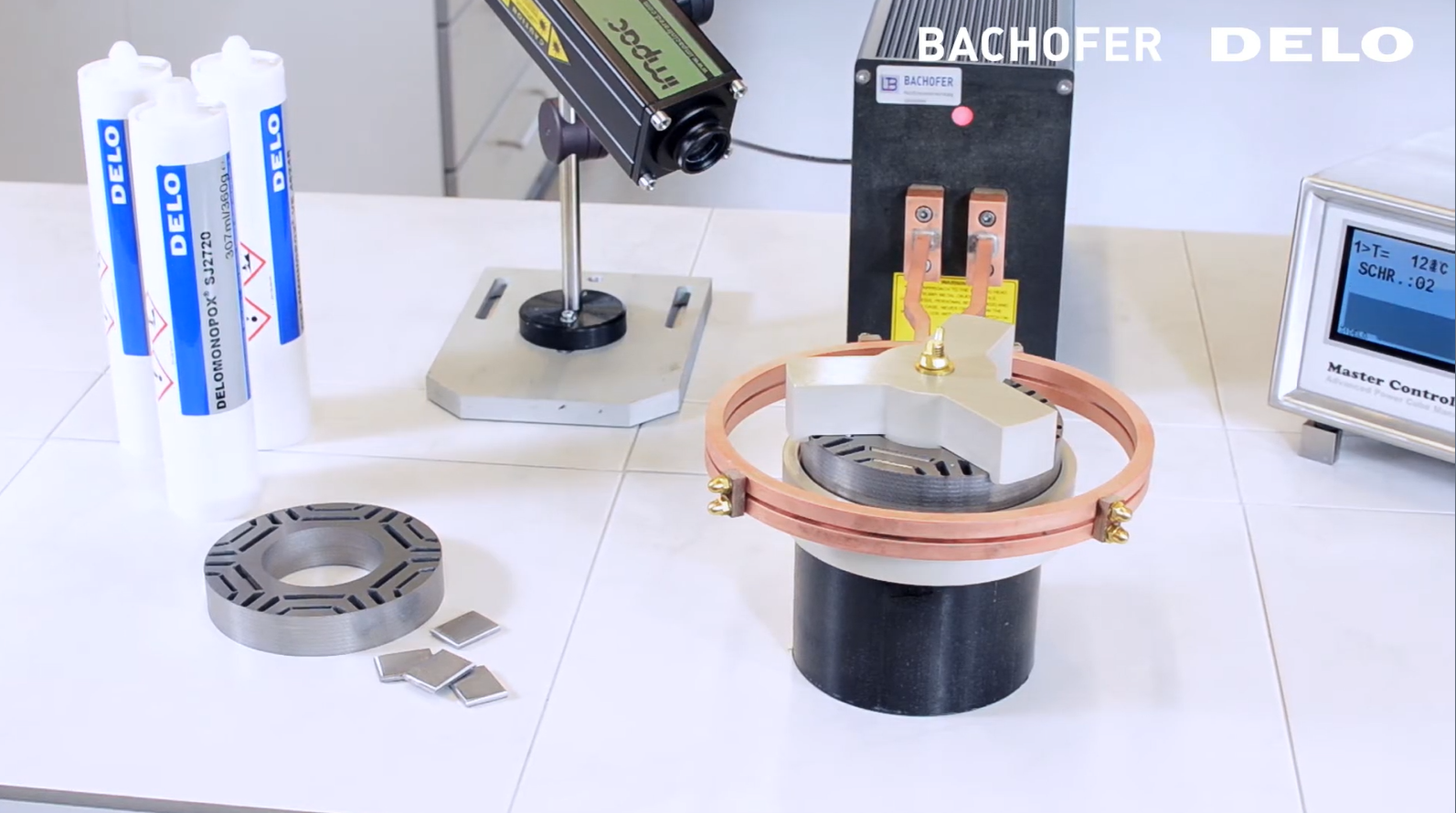
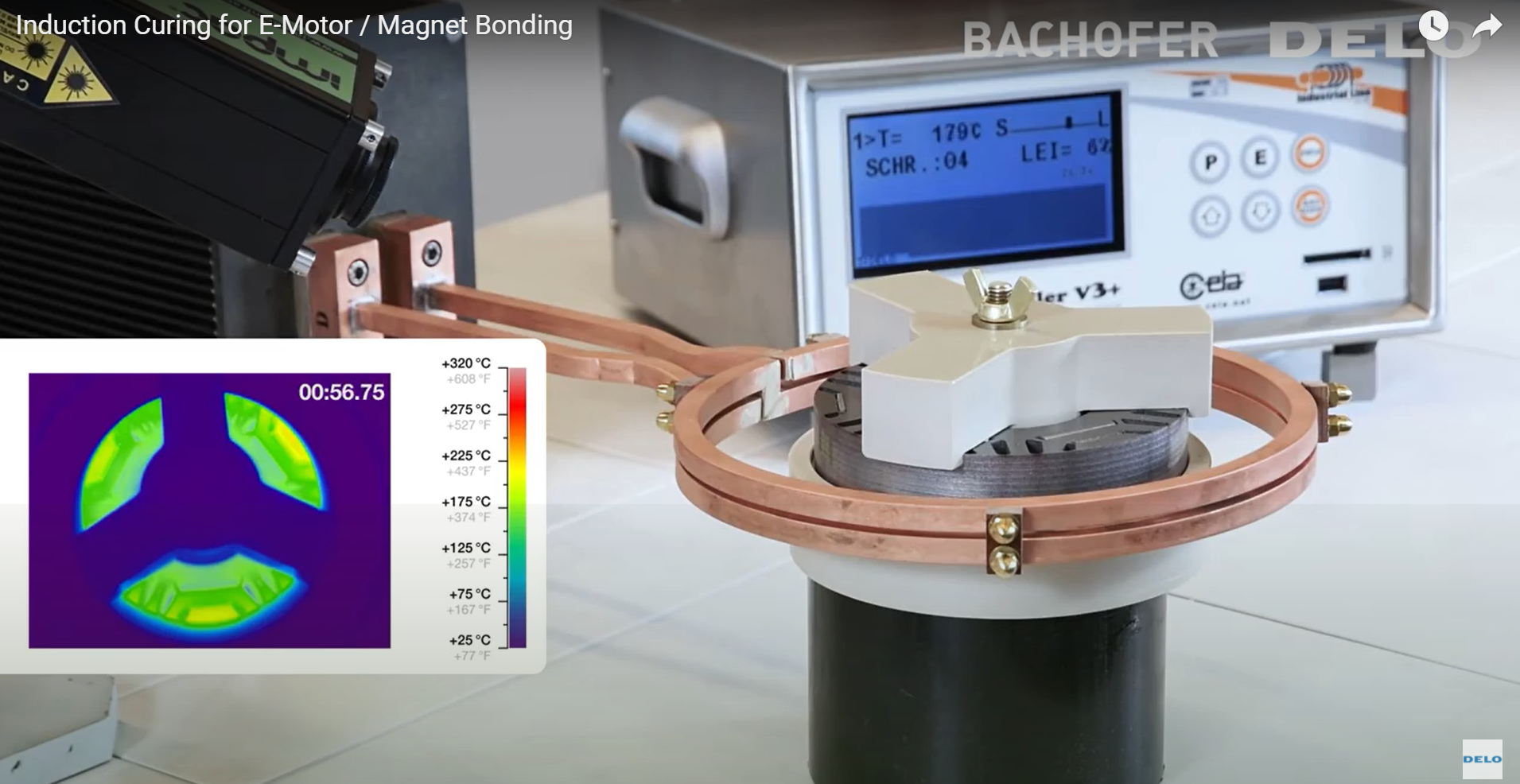
Electric motors are increasingly popular on the market today, being used more and more, especially in vehicles. To optimize the performance and durability of the engine, manufacturers are gradually replacing the mechanical assembly of engine parts with screws by using glue. For example, bond magnets to the housing of electric motors.

See more: DELO Glue APPLICATION IN ELECTRIC ENGINE E-MOTOR
The necessary heat used to cure the adhesive
Completely drying the adhesive for metal parts such as electric motors requires a lot of time and cost. About 2-component adhesives typically take 24 hours to 7 days at room temperature to reach maximum strength. However, in the production process, the curing time of the adhesive needs to be adjusted to the time of the mass production cycle, which means that it must cure quickly with high reliability.
The great ideal solution is that the adhesive will cure within seconds using UV light. But this method only applies to translucent to transparent components, allowing UV light to pass through, and for visible locations, the temperature curing solution is the most optimal.
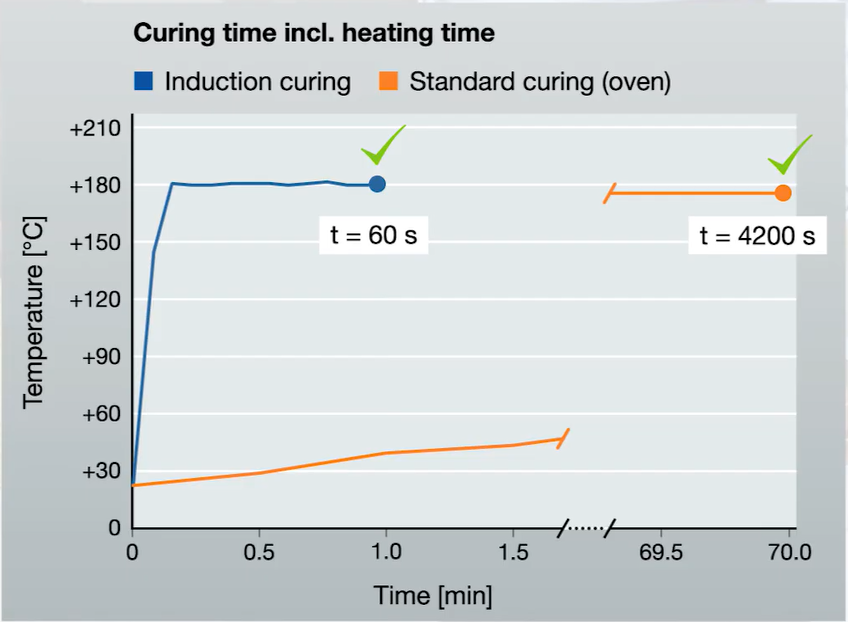
Normally, heat curing is carried out in a convection oven with a time of 15 ~ 60 minutes. Consumes a considerable amount of heat, and the thermal efficiency is really low.
Electromagnetic induction heat curing is an effective alternative to ovens.
This method improves heat curing in just a few minutes and is highly efficient and effective for conductive metal components.
What happens during glue curing with induction heat?
The great ideal solution is that the adhesive will cure within seconds using UV light. But this method only applies to translucent to transparent components, allowing UV light to pass through, and for visible locations, the temperature curing solution is the most optimal.
Normally, heat curing is carried out in a convection oven with a time of 15 ~ 60 minutes. Consumes a considerable amount of heat, and the thermal efficiency is really low.
Electromagnetic induction heat curing is an effective alternative to ovens.
This method improves heat curing in just a few minutes and is highly efficient and effective for conductive metal components.
What happens during glue curing with induction heat?
During induction heating, a metal component such as an electric motor housing is partially or fully exposed to the alternating electromagnetic field generated by a current-carrying coil. This magnetic field induces eddy currents in the material, which are in the opposite direction of the original currents (Foucault currents) and have the effect of heating the material. The induced current helps to heat the conductive components very quickly and evenly and greatly reduces the heating time, thereby accelerating the curing of the adhesive. The heating process can be even accelerated in the case of ferromagnetic substrates.
How is heat generated in adhesives?
The surface of conductive metal components heats up very quickly due to the induced current and heat transfer to the adhesive. In the case of non-conductive components such as ceramics or plastics, etc., suitable additives such as metal powders will be added to the adhesive so that the glue can conduct electricity. This directly heats the adhesive layer and thus allows it to cure faster.
In contrast to conventional heating processes, heat is generated directly in the adhesive, which then cures within minutes or even seconds. Unlike thermal curing methods such as radiation or convection, induction curing generates heat within the conductive component sample itself.
Because the heating time is reduced, while the temperature is still satisfactory as in the oven curing process, the adhesive molecules will be smaller and more mobile, which increases the cross-linking in the polymer network of the adhesive, thus maximizing the adhesion strength.
Temperature is monitored by a thermal camera (pyrometer) and is controlled via a controller on the inverter.
Advantages - disadvantages of glue curing by electromagnetic induction
Advantages:
A clear advantage of induction heating over other methods is that it allows for targeted heating and curing of areas that need bonding. Flexible layout for large, difficult to move parts, while only needing to bond a small part on it.
Compared with curing in an oven, electromagnetic induction does not take time to heat up all components, thus greatly reducing heat loss and costs.
Furthermore, the production cycle time is significantly reduced thanks to the rapid heating. Operations can be monitored by a specific process control system, which can be directly integrated into the production line, shortening the production cycle time and ensuring the accuracy of the process. Adhesive helps to reduce energy consumption.
Disadvantage:
Induction heating is limited by the depth of penetration. Components to be cured require a solid one. In addition, the components must be more symmetrical to ensure uniform heating, and the distance between the inductor and the component must be the same from any point.
Complicated geometries make heating less efficient because the different distances between the coil and the component lead to the electromagnetic field attenuating as the distance increases.
Conclude
Thus, it can be said that induction heating is a perfect alternative to the traditional oven because:
- Helps reduce curing time, ensuring time requirements for a production cycle.
- Ensure heating requirements for local areas with adhesive, avoid affecting other parts and also reduce heat loss to heat unnecessary parts.
- High heating efficiency helps to minimize energy costs in production.
Another important aspect is the potential for energy savings due to heating within seconds. Depending on the application in question, the induction heating process will need to be optimized in terms of space, time, frequency, etc. to match the glue drying temperature requirements.
Currently, this method has been applied at many DELO customer factories, and is also widely applied to many DELO glues such as MONOPOX, DUOPOX, DUALBOND, ...
Contact HUST Vietnam for more detailed information.
HUST Vietnam is proud to be the exclusive distributor of glue, dispensing equipment, UV glue curing lamp, and technology transfer from DELO in Vietnam!
