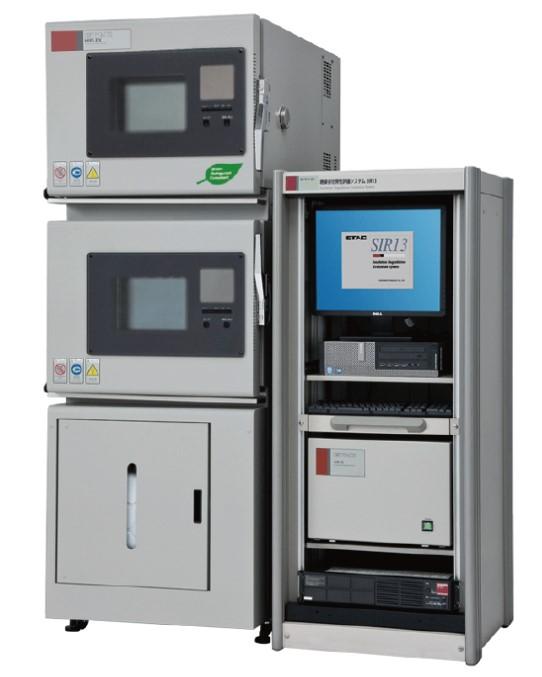

SIR13 – Insulation Degradation Measurement System for PCB Reliability Evaluation According to International Standards
10:54 - 05/02/2026
SIR13 (Insulation Degradation Measurement System) is a dedicated test system designed to evaluate surface insulation resistance (SIR) degradation on printed circuit boards (PCB, FPC). It is particularly effective for detecting electrochemical migration (ECM), a major failure mechanism that can lead
What is HALT and HASS testing?
Guide to choose Thermal shock test chamber
How to choose Temperature & Humidity test chamber?
Introduction to the SIR13 Insulation Degradation Measurement System
SIR13 is designed for high-speed, high-accuracy SIR measurement, making it suitable for both R&D laboratories and production quality control environments.
Key Technical Features
High-speed measurement down to 20 ms per channel
Supports up to 128 measurement channels at 250 V
Equipped with SMU (Source Measure Unit) boards for precise detection of leakage current and instantaneous ECM events
Supports per-pin bias and common bias measurement methods
Wide voltage range from 25 V up to 10 kV (depending on the measurement board)
19-inch rack-mount design, scalable and easy to integrate with environmental chambers
Compared with conventional SIR test systems, SIR13 enables simultaneous measurement of multiple samples, significantly reducing test time and minimizing the risk of missing short-term or intermittent short-circuit events.

Principle of Insulation Degradation and ECM Measurement
By continuously measuring insulation resistance under high temperature and high humidity conditions, SIR13 enables early detection of leakage current and short-circuit formation, providing a reliable method for assessing the long-term reliability of PCB assemblies and electronic components.
This application note is prepared in accordance with widely recognized international standards, including:
IPC J-STD-004C – Flux qualification
IPC J-STD-001 – Requirements for soldered electrical and electronic assemblies
IPC-TM-650 (2.6.3.7) – Surface insulation resistance (SIR) and ECM test methods
Typical test conditions: 85°C / 85% RH, DC bias 50–100 V, test duration up to 168 hours
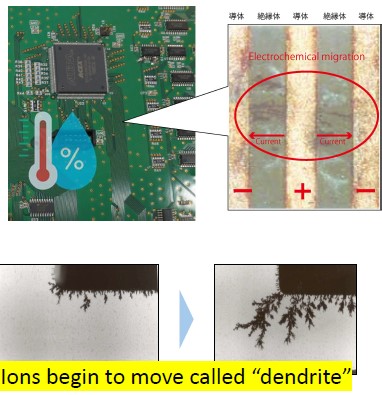
ECM Mechanism
Under the influence of DC electric field and moisture
Metal ions migrate from the anode to the cathode
Metallic dendrites are formed
Resulting in leakage current increase and short-circuit failure
SIR13 records data in real time and provides comprehensive analysis through Windows-based software, with support for temperature and humidity sensor integration to synchronize environmental conditions with electrical measurements.
Standard-Compliant Test Procedure Using SIR13
1. Sample Preparation
Use IPC-compliant test coupons
Comb-pattern electrode structures
Electrode spacing: 0.1 – 0.5 mm
Apply flux or soldering processes when evaluating manufacturing-related effects
2. SIR13 System Setup
Select the appropriate measurement board (e.g., 250 V per-pin 16-channel board)
Install up to 8 measurement boards in a single 19-inch rack
Configure control and analysis software
Interface with environmental chambers (e.g., ESPEC, ETAC)
3. SIR Testing Conditions
Environmental conditions:
85°C ±2°C / 85% RHDC bias voltage: 50–100 V (applied for at least 1 hour prior to measurement)
Measurement voltage: 100 V DC
Test duration: 24 – 168 hours
Acceptance criterion: SIR ≥ 10⁸ Ω in accordance with IPC J-STD-004C / IPC-TM-650
4. Data Analysis
Plot SIR versus time
Failure is identified when:
SIR drops below 10⁸ Ω
Short circuit occurs (<100 Ω)
Failure mechanisms are evaluated as ECM-related degradation
5. Reporting
Export test data in CSV format
Optional correlation with microscopic images of dendrite growth
Suitable for QA documentation, customer reports, and certification purposes
Benefits and Referenced Standards
Compliant with:
IPC-TM-650 for SIR and ECM testing
IEC 60068 for environmental testing
Enables early prediction of PCB and electronic component reliability
Ideal for applications in:
Automotive electronics
Industrial electronics
High-reliability electronic systems
Widely adopted in Japan, China, and Taiwan by PCB and PWB manufacturers
Early detection of insulation degradation helps reduce short-circuit risks, improving overall product safety and quality
