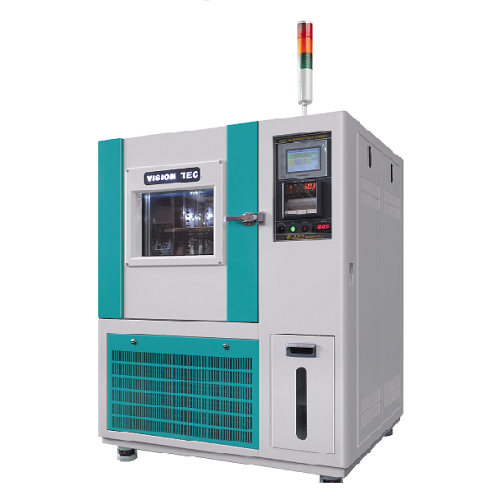

How to choose Temperature & Humidity test chamber?
16:42 - 07/07/2020
Choosing the right temperature and humidity test chamber to suit your needs is often a difficult task. Therefore, to help customers know how to choose suitable equipment, HUST VIETNAM will give important information to guide the selection of the most suitable temperature and humidity test cabinet.
Basic steps in HALT and HASS testing to improve product reliability
What is HALT and HASS testing?
Guide to choose Thermal shock test chamber
HUST VIETNAM provides the most important information possible for customers to understand the main functions of the temperature and humidity test cabinet to enable customers to choose the most accurate products.
TWO BASIC FACTORS FOR SELECTING TEMPERATURE & HUMIDITY TEST CABINET:
- Performance of the product to be tested
- The tests it will have to go through (Temperature, humidity, time, cycle ...)
TEST STANDARDS:
Temperature and humidity tests are usually described in specific industry standards (IEC, DIN, ISO, ASTM, MIL, JIS, KS, TCVN etc.) or proprietary standards (FCA, FORD, ESA, BMW , etc.).
Knowing the standard of testing the product will go through is essential to choosing the humidity temperature testing cabinet and its accessories. Therefore, it is best to have as much information as possible about the tests to be performed before selecting the chamber model; Usually a pre-selection starts with the following information:
- Temperature range
- Temperature exchange rate
- Humidity range
- Cabinet volume and sample
- Sample weight
- Performance of the product to be tested

- Temperature range:

The specification tables of the climatic chambers define the minimum (min) and maximum (max) temperatures achieved. Almost all climatic chamber manufacturers set the maximum temperature at + 150° ~ + 180°C, although if required this can be extended to + 200 ° C as a option. Although the maximum temperatures are almost always the same, the minimum temperatures of the chambers using a mechanical cooling system allow them to be divided into two broad categories:
✓ Single cooling system -20° ~ -40°C
✓ Dual cooling system -50° ~ -70°C
However, we do not need to go into the detailed differences in the operation of the two cooling systems, but it should be clear that the dual refrigeration system consists of two cooling systems, consisting of two separate units. arranged in series so that very low temperatures can be reached.
Sometimes, a humidity temperature test cabinet with a dual refrigeration system is chosen not to have a particularly low temperature below the desired cooling level, but to have a fast cooling rate at a low temperature.
2. Temperature exchange rate

The rate of increase or decrease in the temperature inside the test chamber is called the temperature exchange rate (expressed in Kelvins or degrees Celsius per minute) and can vary greatly from model to model. , from 1.5°C/min to 20°C/min
The rate of temperature exchange obviously depends on the cooling capacity of the compressor and the heating of the heating rod installed in the chamber. In other words, the stronger the compressor, the faster the cooling rate and the more heat bars are installed in the chamber, the faster the heating rate.
The temperature exchange rates given in the humidity temperature test cabinet specifications table usually refer to the equipment performance with the test cabinet being empty (i.e. without the test piece).
3. Humidity range

In the temperature and humidity test cabinet specifications table, we check the climatic range, i.e. the minimum and maximum temperatures in which the device can control and adjust humidity values, times turn is indicated by
✓ Temperature range for climate test: + 10°C to + 95°C
✓ Humidity range: 10%RH to 98%RH
In order to better understand the humidity values that can be achieved in a climatic chamber, it is necessary to understand that the relative humidity (RH) that can be attained in the chamber is temperature dependent. For this reason, to accurately determine the climatic range, it is also necessary to refer to the dew point (evaporation point).
To make it clearer and easier to understand, a humidity diagram like the one below is provided with the technical datasheet, which shows the possible humidity values for each temperature value:
* Relative humidity:

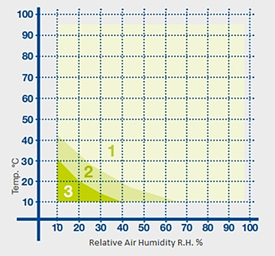
In this diagram, there are 3 areas:
Zone 1 indicates the area for continuous testing with a dew point between + 10°C and + 94°C (Standard Range). According to the baseline of Zone 1, we can easily find the minimum humidity value for each temperature value in the climatic range: for example, with T = 20°C, the minimum moisture value possible in the chamber as RH = 40%.
Zone 2 represents the temperature and humidity combinations that can only be reached for limited time (dew point down to -3°C in a short time).
The T and RH combinations in Zone 3 are values that can be achieved with a dedicated device for very low humidity testing including a dry air spray system (dew point -40°C).
4. Volume

The main information to consider regarding the product to be tested is: product size, product shape and weight of product under test.
The size of the product allows you to determine the volume of the test cabinet, which is large enough to accommodate comfortably. It is generally best practice that the size of the test piece should not exceed one-third of the volume of the test chamber, although special consideration should be given to the shape of the product under test. In all cases the air shall be able to circulate freely to ensure that the variation and uniformity of temperature are almost equal (within the tolerance specified by the test) over the entire surface. of the test sample.
5. Sample weight

The weight of the test piece is also a very important parameter, as large volumes can adversely affect test performance: the performance of the climatic chambers, such as the temperature slope, calculated and specified with empty chamber, i.e. without any mass inside the test chamber. Therefore, when the required value of the required temperature exchange rate for the test piece is close to the value of the temperature exchange rate given in the technical data sheet (with empty chamber), it is necessary to carry out a home inspection. supply room.
Weight is a parameter that must be taken into account for another reason: the test cabinet racks are designed to support specimens up to a certain weight. Therefore, it is best to check the rating plate for what the maximum weight of the test piece is.
If the test piece exceeds the maximum permissible weight, the cabinet accessories include a reinforced bracket or bracket.
6. Performance of the product to be tested
a. The test sample works when tested:

When the test piece is connected to a power source (active prototype), it can dissipate heat. In some cases this may be insignificant, while in other cases it should be taken into account, as it may affect chamber performance, as specified above is often indicated with Empty chamber i.e. no volume and no heat dissipation.
Therefore, when the test piece is in operation, the chamber shall remove the heat radiating from the test piece without affecting its performance, in which case the test values are met.
b. A special case

There are also special circumstances in which the test piece may release flammable, explosive, toxic and / or corrosive substances or substances that may generate potentially hazardous gases, depending on the temperature range. they can be attained.
In this case, the client is required to consult with HUST VIETNAM to accurately assess the test-related risks.
Above are all instructions on selecting a temperature and humidity test cabinet that HUST VIETNAM sends to you.
Hotline: 0968 035 168 or Email: info@hust.com.vn
THANKS YOU!
